Digital twin technology is an increasingly popular tool among companies of all sizes in various industries. Global industries have undergone a significant technological transformation because of the power of digital twins, which comes from physical space and virtual world connections. This digital representation can track the behavior and performance of its real-world counterpart over time.
With Digital Twins, businesses can simulate and optimize their operations, predict failures, and improve the efficiency gains of their processes. Likewise, digital solutions providers such as NCS can use digital twin technology to help other businesses digitalize their operations.
Table of Contents
What is Digital Twin?
A digital twin is a digital replica (copy) of physical systems, digital products or services and is updated in real-time. Digital twins provide digital data and analytics to provide performance insights and can be used in many industries to optimize operations and predict risks accurately.
Digital twin technology has been used in the aerospace and defense industries for years. Michael Grieves coined the term “digital twin” in 2002 to develop digital twins for space programming. The technology gained notoriety when Grieves introduced digital twin technology. Since then, digital twins have become a staple of digital transformation initiatives across many industries, including manufacturing, retail, and healthcare.
How Digital Twin Works
At the heart of digital twin technology is digital computing. This is where digital twins got their name, as digital twins are digital replicas of physical systems. Digital twins are created by Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies using digital modelling tools such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD).
Digital twins connect the physical and digital worlds using digital sensors and interfaces. The digital twin captures the data from digital sensors connected to the physical entity, which is then processed by an analytics engine to create meaningful information about the real-world system. This data can be used to make informed decisions that optimize operations and processes.
The Phases of Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology goes through four distinct phases.
The first phase is digital model creation, where digital models are created using digital modelling tools like CAD. The digital model captures the design and behavior of the physical system.
In the second phase, digital twins are deployed by connecting digital sensors to the digital model. This is done using digital interfaces such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Sensors. The digital sensors capture real-time data from the physical system.
The third phase involves digital twin analytics, where digital twins serve as a platform for digital analytics. This digital analytics engine processes the data from digital sensors and provides insights that can help optimize operations and processes.
The fourth phase of digital twin technology is digital twin optimization. This phase uses digital analytics to optimize the digital model by improving design, performance, and maintenance areas. This digital optimization can minimize downtime, maximize production and resource utilization, and reduce operational costs.
The Principle Behind Digital Twin Technology
To better understand the value digital twins bring to businesses, it’s essential to know the principle behind digital twin technology. Digital twins are digital replicas of physical systems that can capture digital data and digital analytics. This digital data can be used to optimize operations, predict failures, and improve the efficiency of the real-world system.
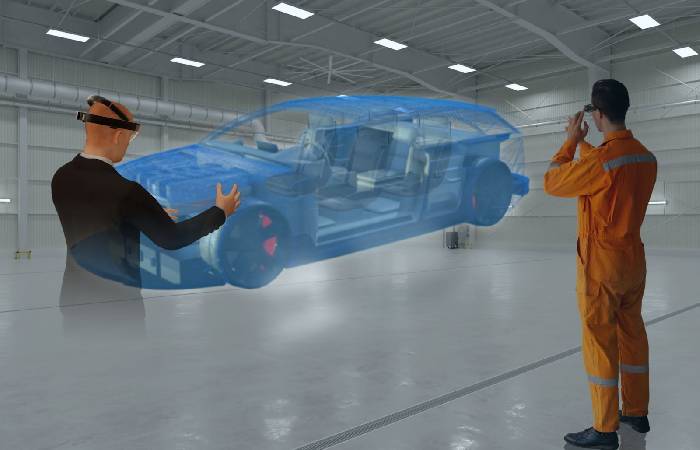

To give you a specific example, consider a building that has already been designed and constructed. Imagine that there is a digital twin of that building from the roof, vents, engineering, and plumbing systems. The sensors from the establishment will provide the digital twin with real-time digital data about the building, such as temperature and humidity levels.
Using digital analytics, digital twins can then offer predictions on how well ventilation is working or when a particular system needs to be serviced. Likewise, sensors on the structural engineering systems of the establishment will provide digital twins with data on where the building is ageing or where there are risks of structural failure. Building owners can then make improvements to prevent this structural failure.
Multiple digital twins can be integrated into an entire ecosystem on a grander scale. For example, digital twins of various industrial processes in a factory can be connected to digital twins of related systems, such as digital twins of machines, marketing, advertising, customer service, and security. This allows businesses to use digital twins as a platform to optimize their digital operations at an enterprise scale.
On a much larger scale, digital twins can be integrated in the future to monitor global environmental conditions and weather events. Data from these digital twins can help anticipate severe weather conditions.
Types of Digital Twins
A digital twin starts with knowledge of physical assets, digital sensors, models, analytics, and optimization. The data gathered from the digital sensors can be used to create various types of digital twins.
The most common digital twins are digital replicas of machines or digital images of entire factories. These digital twins provide a digital representation of the devices or factories, capturing digital data and digital analytics to provide insights into performance.
Digital twins can also be used to replicate digital products, digital services, digital markets, digital customers, and digital users. For example, digital twins of digital products or services can be used to monitor digital performance, digital usage patterns, digital user engagement, digital pricing, digital advertising campaigns, and digital promotions. This data can be used to optimise digital operations and digital user experiences.
An individual digital twin can capture digital data and digital analytics on a person’s digital activities, digital preferences, digital buying habits, digital health patterns, digital lifestyle patterns, and digital behaviors. This digital data can provide digital insights on digital customer service, digital marketing campaigns, digital health interventions, digital lifestyle changes, and digital engagement opportunities. Another type of digital twin is a digital replica of a person.
Conclusion
In the future, other industries will use digital twins at a granular level to improve their operations further. As technology continues to evolve and mature over time, so will the potential application of digital twins. With the right implementation plan and digital resources, digital twins will continue providing digital insights and analytics to improve digital operations in many industries.
The possibilities of digital twins are limitless, and the potential for digital transformation is tremendous. Digital twins can help businesses become more efficient, agile, and effective—transforming the way we do business today!