DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Conformance and Reporting. It’s a standard that allows domain owners (like you!) to create policies that tell the email servers in your organization how they should handle emails from other domains.
Table of Contents
Why should I care about DMARC?
Email spoofing is one of the most general methods cybercriminals use to gain access to your data. Spoofed emails can look very legitimate, so you must ensure that any emails you receive from outside sources are legitimate before taking action. DMARC helps you verify the legitimacy of an email’s sender.
Email phishing is one of the most general ways hackers can access your company’s sensitive information. Spoofing usually happens when an attacker sends an email from a legitimate sender, like your company address or someone else’s email address. This can trick recipients into opening attachments or clicking links containing malware or malicious code.
DMARC helps prevent email spoofing by enabling organizations to detect and prevent fraudulent emails from being sent from their domains. It also allows organizations to monitor and report on those emails that pass through their systems.
Learn more about what is DMARC.
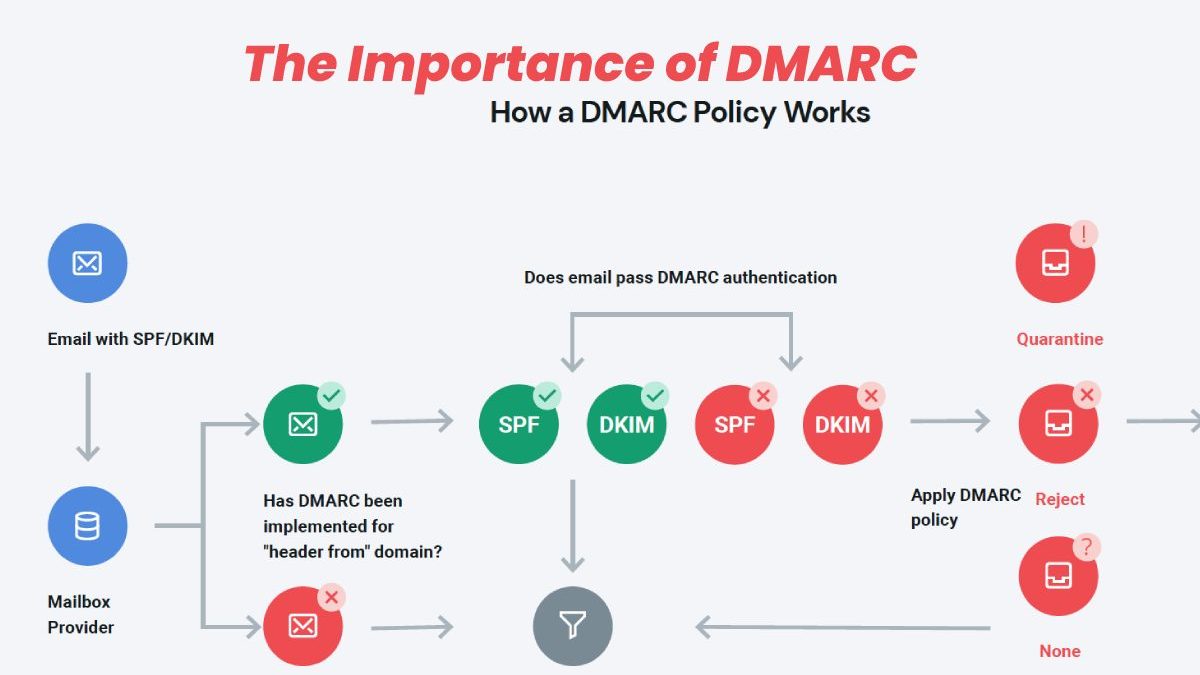
How does it work?
When your company sets up DMARC, it will have three policy options: none (which means no one can send email using your domain), quarantine (which means suspicious emails are sent to a spam folder), or reject (which means those emails are blocked entirely). When someone wants to send you an email using your domain, they’ll send it through an authorized mail server (like Gmail or Outlook), which will check its settings against yours before delivering it.
You can verify if your DMARC record is functioning as it should be checking your DMARC record using a DMARC checker.
How do I enable DMARC?
1. Set up SPF for your domain
Before the advent of SPF and DKIM, people could make their emails look like they came from other people’s accounts. They did this by faking an email “From” address, which meant that all kinds of shady business were happening in your inbox: identity theft, phishing scams, and more.
In response to this problem, SPF (Sender Policy Framework) was created to make it easier for mail servers to determine who sent an email. It works by listing all of the domains that can send mail on behalf of your domain name (e.g., [email protected]). SPF also takes into account whether or not those domains are authorized to send messages on behalf of your domain.
Check if you have an SPF record already with a free SPF record check.
2. Set up DKIM for your domain
DKIM is a method of signing emails to verify their authenticity. DMARC allows you to set up rules for how your organization handles email that fails DKIM verification or fails DMARC policies. To setup DKIM for your domain you need to enter your domain name and DKIM selector in the generator tool to create your DKIM signature keys.
Conclusion
With DMARC, you can:
- Tell recipients about fraudulent messages before they open them
- Improve the domain reputation of your brand
- Prevent spam from being delivered as legitimate mail
DMARC helps prevent domain impersonation by allowing you to set up policies that specify how your domain should be validated when someone sends an email on its behalf of it. For example, if you don’t want people to be able to send emails from your domain but aren’t sure how to stop them, DMARC can help you do that.
DMARC also helps improve the accuracy of reporting on emails sent from your domain. If someone else is impersonating you, DMARC will let you know so that you can take action against them, highlighting its importance in cyber security.