Table of Contents
Stream Cipher Definition
A Stream Cipher is an encryption method and is part of symmetric cryptography. With stream ciphers or stream ciphers, the data encrypted in one piece.
This type of encryption is not that common. Block ciphers are used much more frequently for symmetric encryption.
Stream ciphers are less well than block ciphers. One reason for this is that block cipher
prefers in the DES and AES crypto standards.
And also, This has led to the neglect of stream ciphers. Block ciphers can also be resource-saving and fast.
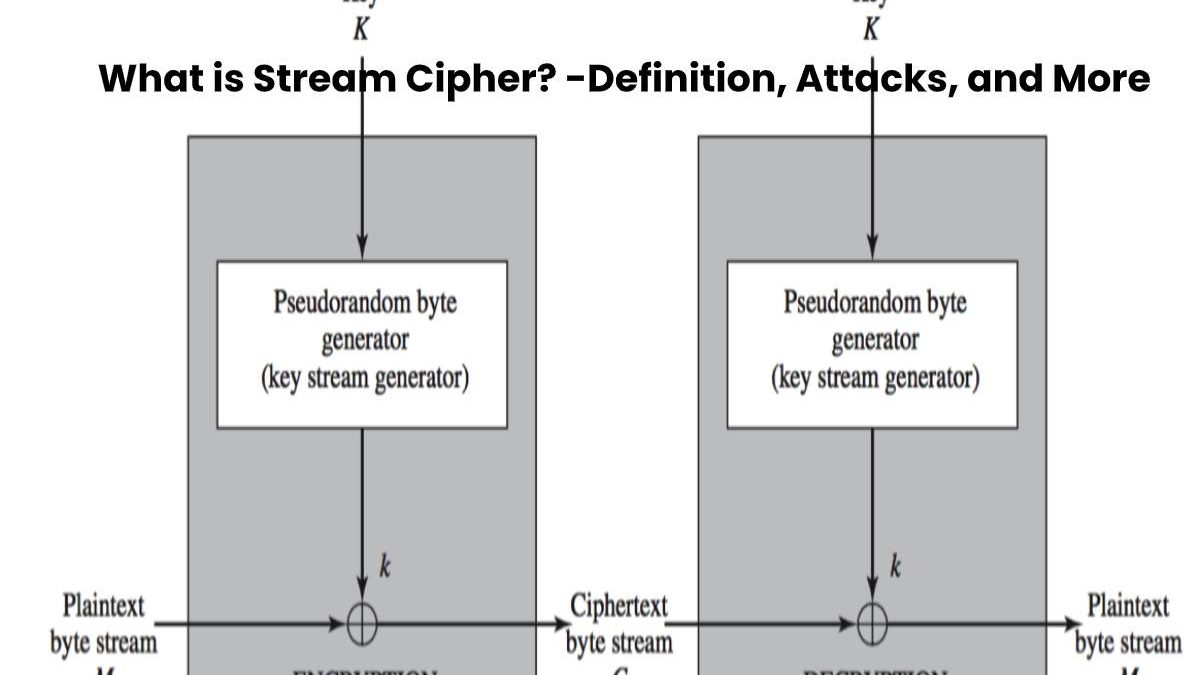
How does Stream Cipher work?
In principle, a random sequence is generated and exclusively or linked with the plain text (logical XOR function).
- The random sequence is a keystream, which generates from a start value from the forward function.
- And also, The starting value can be secret but does not have to be. A known, non-secret starting value refers to as an initialization vector (IV).
- It must be in a key-dependent advance function because an attacker can find out the start value and the functioning of the advance function.
- Senders and receivers only have to make sure that they use a different random sequence for each encryption — for example, a random number or a counter.
- And also, The recipient can exclusively-or-link the ciphertext with the same random sequence and the ciphertext and gets the plaintext again.
What are the Attacks on stream ciphers?
- Ciphertext-only attack
- Known-plaintext attack
- Chosen-plaintext attack
An attack on a stream cipher is based on the attacker knowing part of the keystream.
Alternatively, an attacker could use differential or linear cryptanalysis.
What are the Advantages of stream ciphers?
Stream ciphers have two primary advantages.
- The keystream can be pre-calculated and buffered, which increases the speed.
- And also, The second advantage is that if there is a bit error in the ciphertext, only one bit in the plaintext is defective.
What are the Disadvantages of stream ciphers?
- The effort for initialization is quite high. For this reason, high speed only achieved with longer plain texts.
- And also, any part of the ciphertext cannot decrypt individually. The complete ciphertext must always decrypt.