Table of Contents
SIEM Definition
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) enables a holistic view of IT security by collecting and evaluating messages from various systems.
It is a software-based technology concept from the field of security management, with which a holistic view of IT security becomes possible.
SIEM represents a combination of Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM).
And also, By collecting, correlating, and evaluating messages, alarms and log files from various devices, and security systems, attacks become unusual patterns.
What are the Principles of Operation in SIEM?
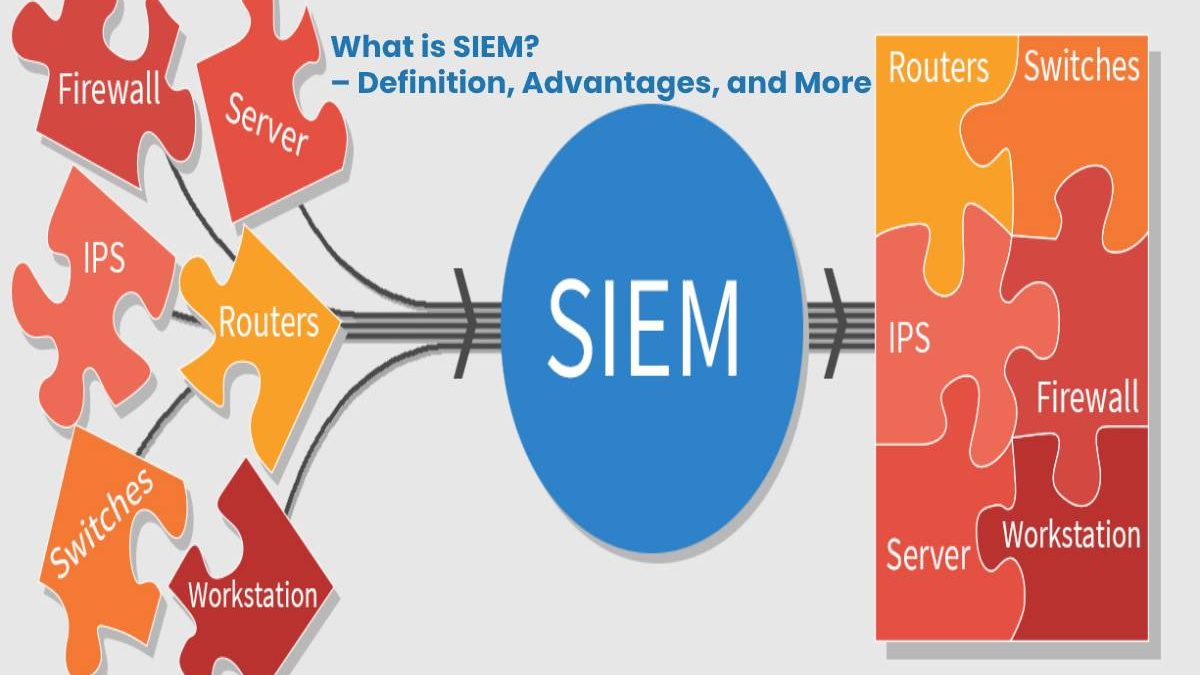
The basic idea of an SIEM is to collect all data relevant to IT security in a central location and to identify patterns and trends through analyzes that indicate dangerous activities.
- Firstly, The data is collected and interpreted in real-time. All information is tamper-proof and audit-proof.
- And also, Typical sources for the SIEM are firewalls, servers, routers, IDS, IPS, and applications.
- Security Information and Event Management ensures the normalization and structuring of all collected data.
- By relating the data records, it is possible to identify intrusion attempts through incorrect login attempts or unauthorized access by the firewall.
- However, Software agents are usually responsible for collecting the data. These forward the information to a central management station.
- And also, The central station is responsible for storing, normalizing, structuring, and evaluating the data.
What are the Goals of [SIEM]?
- The SIEM provides an overview of security-relevant events in IT environments and helps to meet legal requirements and compliance regulations of IT security.
- And also, Both the real-time reaction to threats and the subsequent detection of security events are possible.
- Automated reports and targeted alarms allow IT security personnel to respond appropriately to the various threats.
What are the Advantages of using a SIEM?
The use of security information and event management has numerous advantages. These advantages include:
- fast and reliable detection of threats
- the quick and appropriate response to security-related events
- And also, Compliance with legal requirements and compliance regulations
- Saving personnel in the IT security environment through automation
- subsequent proof of security events
- And also, Tamper-proof and revision-proof storage of all security-relevant events