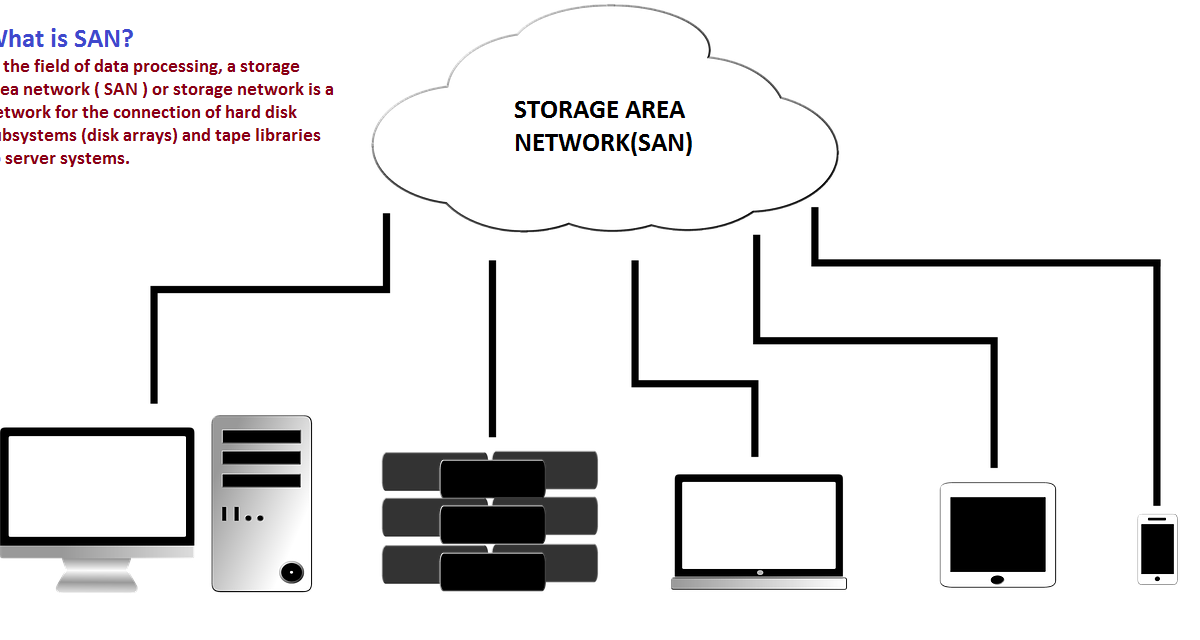
Storage Area Network Definition
In the field of data processing, a storage area network ( SAN ) or storage network is a network for the connection of hard disk subsystems (disk arrays) and tape libraries to server systems.
Storage Area Networks blueprint serial, continuous, high-speed, high-volume data transfers.
Today, for high-availability, high-performance installations, they are based on the implementation of the Fiber Channel standard, while for SMEs, cost considerations also apply to IP.
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) is an extension of SAN, where disk storage capacity allocates to a server over a network, but can also dynamically allocate to a server within operational limits.
What are the functional principles of SAN?
- The SAN is designed to address the management issue of dedicated hard drives in server systems or network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
- The Ethernet, via which the NAS systems connect to the servers or the clients, with its small frame sizes and relatively high protocol.
- SANs today are mostly made via fiber-optic cables; the system uses the Fiber Channel.
- Today they work with transfer rates of up to 16 Gbit / s.
- They use a unique protocol adapted to the mass storage requirement, transfer rates of 1.6 GB / s are possible.
- This sample SAN consists of two switches, each forming its fabric. The servers connect to each fabric with one host bus adapter each, as well as the disk array.
What is SAN architecture?
- The Storage Area Network designed to run parallel on the LAN. The SAN provides itself to the LAN as whole mass storage.
- Basically, The servers see the SAN as a kind of data pool, which divides into separate logical units.
- Multiple redundant paths between the user and the data protection against possible failures and data jams.
- The system architecture of a SAN has a comparatively complex effect on outsiders.
- In general, a distinction made between transmission systems, access protocols, tunneling, and transport protocols.
- And also, The differences are mostly fluent because some techniques have cross-tasking functions.