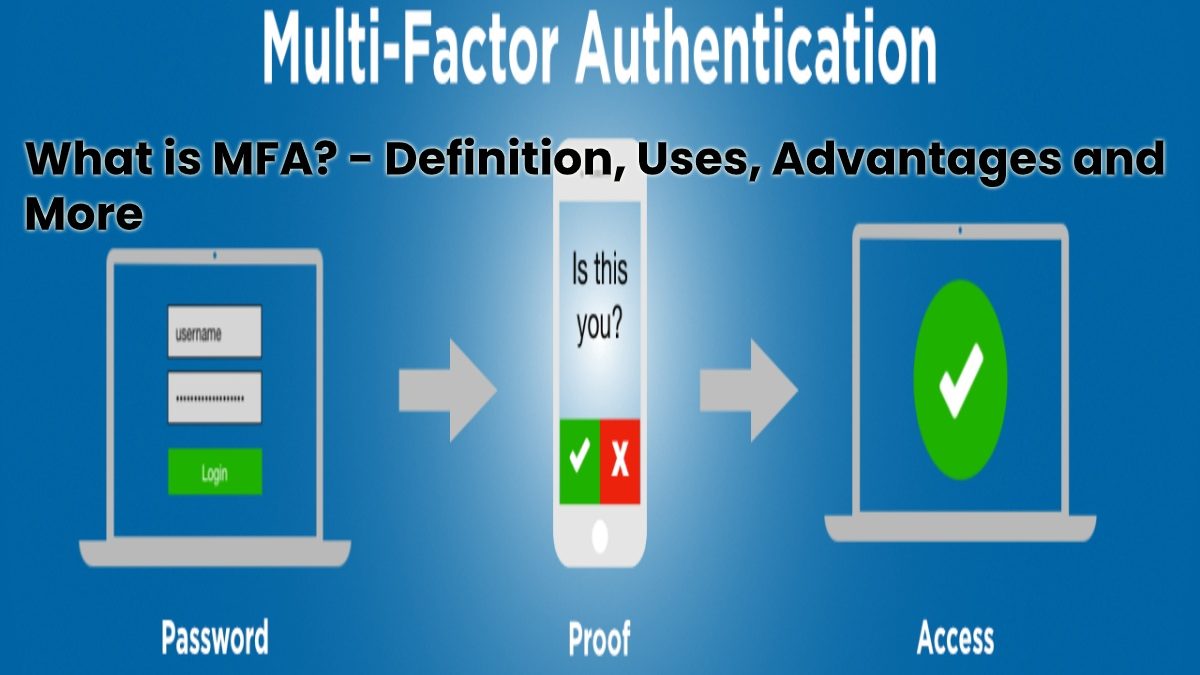
What is multifactor authentication?
MFA, or Multi-Factor Authentication, is a security process that requires multiple authentication methods to access a system or application.
MFA is a safer form of user verification because the user must provide two unrelated credentials to access it. Typically, this involves three possibilities:
- Something users know (i.e., a password or passwords)
- Something the user of (i.e., a security token, access card, etc.)
- And, Something the user is (i.e., a biometric verification such as a fingerprint or facial recognition)
Here are some examples of authentication scenarios involving multi-factor authentication:
- Swipe a card and enter a pin to access a server room.
- Access a website using a password and a one-time password (OTP) that is sent to your smartphone via a text message.
- Swipe a card and scan a fingerprint.
- Attach a USB token to your computer that generates a one-time password and uses a known password.
Uses of MFA
- The use of multi-factor authentication mechanisms refers to the application of at least two authentication factors.
- This allows for reliable and strong authentication. This is more difficult to compromise because several shared secrets must be known to authenticate.
- Thus, a multi-factor authentication system is, from a security point of view, more difficult to defraud than a simple authentication system.
- Indeed, the attacker would have to discover/reproduce/obtain several things such as the shared secret (something you know) as well as the token (something you have) and reproduce what you are (biometrics).
- It’s best to use multi-factor authentication to protect high-risk, high-stakes information.
What are the advantages of multi-factor authentication?
MFA is a clear security reminder as it eliminates stolen or uncovered passwords as a major threat. And also it makes it much more difficult for potential data thieves to steal your identity or information.
It can also significantly reduce the damage caused by phishing since any phishing attack will likely only reach the user’s password or username, which will not be enough to gain access to a system protected by the Internet — multifactor authentication.
Besides, with MFA tools such as Duo or Okta, deploying and managing multi-factor authentication can be simple and easy to manage.