Table of Contents
Definition Apache
Apache HTTP is a free Server, open-source web server software for Unix platforms with which 46% of websites worldwide run. [Apache] is developed and maintained by Apache Software Foundation.
Apache allows website owners to serve content on the web, hence the name “webserver.” It is the oldest and most reliable web server, with the first version released more than 20 years ago, in 1995.
When someone wants to visit a website, enter a domain name in the address bar of your browser. Then, the webserver sends the requested files acting as a virtual deliveryman.
Web hosting infrastructure, Hostinger uses Apache in parallel with NGINX, another web server software. This setup allows us to get the best of both worlds. It dramatically improves server performance by compensating for the weaker sides of one software with the strengths of the other.
What is a web server?
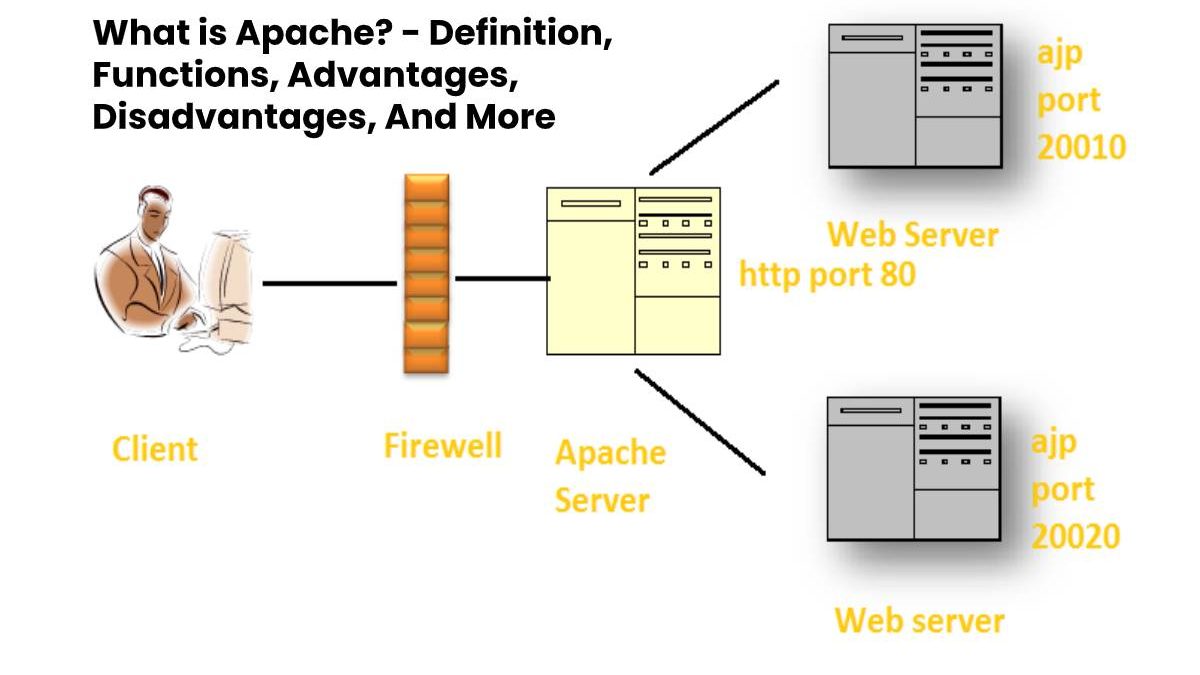
A web server is a computer program that processes a server-side application by accessing files stored on a physical server with the machine client.
It acts as an intermediary between the server and the clients’ machines. It extracts the content from the server at each user request and sends it to the web.
The main challenge of a web server is to serve many different users of the web at the same time, each of whom requests different pages. They process files written in different programming languages like PHP, Python, Java, and others.
They convert them into static HTML files and deliver these files to the web users’ browsers. Web server is the tool responsible for the proper communication between the server and the client.
How does the Apache webserver work?
Although Apache is called a web server, it is not a physical server, but rather a software that runs on a server. Your job is to establish a connection between a server and the browsers of website visitors (Firefox, Google Chrome, Safari, etc.) while sending files between them (client-server structure). Apache is a multiplatform software, so it works on both Unix servers and Windows.
Apache has a module-based structure; therefore, it is highly customizable. The modules allow server administrators to enable and disable additional functionality. Apache has security modules, caching, URL rewriting, password authentication, and more. You can also adjust your server settings through a file called .htaccess, which is an Apache configuration file compatible with all Hostinger plans.
Apache vs. other web servers
Although Apache is the most used, it has many alternatives and rivals.
Apache vs. NGINX
pronounced as Engine-X, it is a newer webserver application first launched in 2004. To date, it has gained great popularity among website owners. It solves the so-called c10k problem, which means that a web server that uses threads to handle user requests cannot manage more than 10,000 connections at the same time.
Because Apache uses the thread-based structure, high-traffic website owners may experience performance issues. Nginx is one of the servers that address the c10k problem and probably the most successful.
Apache v/s Tomcat
Since [Apache] Software Foundation Tomcat web, its official name is [Apache] Tomcat. It is also an HTTP server; however, it works for Java applications instead of static websites. Tomcat can run several different Java specifications, like Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages (JSP), Java EL, and WebSocket.
Pros and cons of Apache
Apache webserver can be an excellent option to run your website on a stable and versatile platform. However, it also has some disadvantages.
Pros
- Free and open-source, even for commercial use.
- Reliable and stable software.
- It Frequently updates security patches.
- Flexible due to its module-based structure.
- Easy to set up for beginners.
- Multiplatform (works on both Unix servers and Windows).
- It comes ready to work with WordPress sites.
- Readily available and Huge community support in case of any problem.
Cons
- Performance issues on websites with too much traffic.
- Too many configuration options can generate security vulnerabilities.