Table of Contents
Database Definition
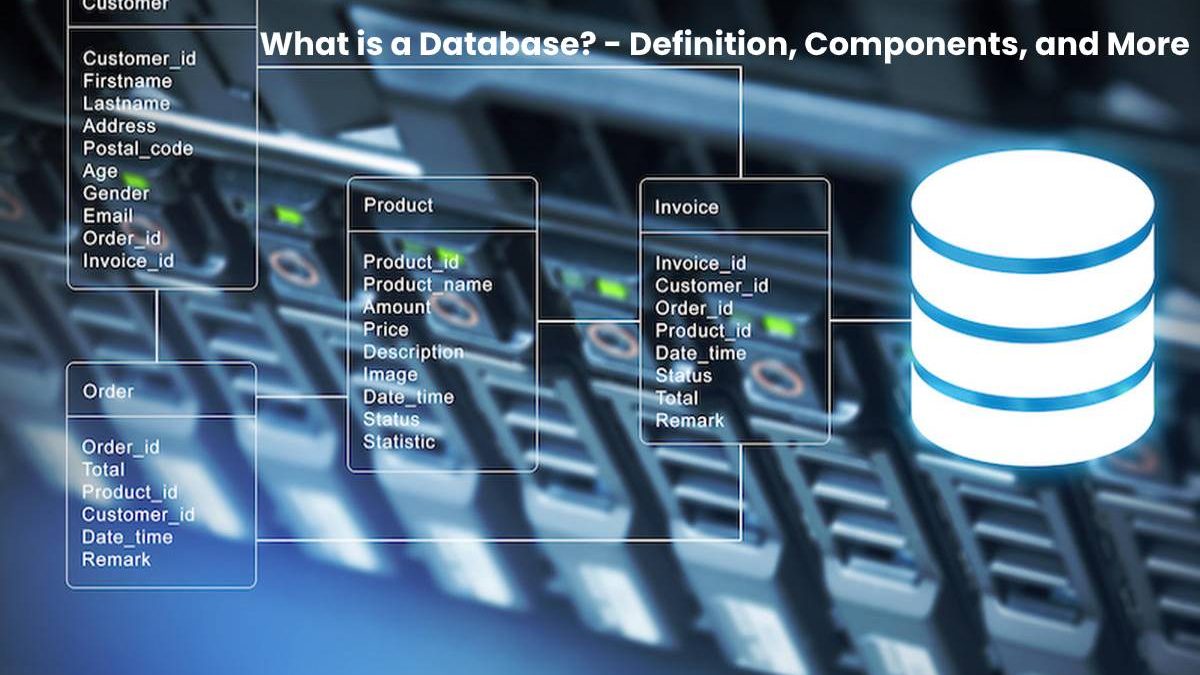
A database is crucial for the functioning of any computerized system. It stores data and makes it available to the user in the desired form.
It consists of two components: the database system, DBS for short, and the Database itself.
And also, It processes large amounts of data efficiently and without contradictions.
Specifically, this means that the Database stores the data permanently and makes it available for use.
The role of the Database: Third pillar of the computer
- The software of a machine is roughly based on three components: the operating system (OS), the applications on the user interface, and the vast amounts of data (data records).
- Some of the data is used for the function of the operating system, the applications require some, and some is data that was deliberately stored by the computer.
- The data must now be bundled and assigned. Also, users, systems, and applications must be able to access them.
- It is precisely the task of it. Every computer, therefore, has not just one database, but many.
What are the two components of the Database?
For the DBS to play its role, it needs two components:
- Database in the narrower sense (DB)
- Database system (DBS, and sometimes it is also called a database management system or DBMS).
The DB divided into different libraries in which the individual data records found.
The DBS handles the communication between the inquirer (the user, a program, or the OS) and the database.
It recognizes which data is required and makes it available in the desired form. The DBS also “sorts” new data into the inventory.
What is the central role of the DBS?
They are highly sensitive; after all, they contain central information. In some cases, attackers can also gain access to actually shielded networks via databases.
- To do this, for example, you must be able to place an appropriate execution code in the proper DBS library.
- Accordingly, the DBS plays a central role. In addition to data management, it must also protect the inventory.
- Databases are, therefore, relational today and no longer hierarchical. It prevents an attack (or an error) from reaching down to the lowest level of the DBS.
- They also work with their languages, which also makes external intervention difficult.
What are the Functions of DBS?
The main functions of DBS are:
- Storage, overwriting and deletion of data
- Data integrity precautions
- Management of metadata
- Data security precautions
- Data protection precautions
- And also, Enabling multi-user operation through the transaction concept
- Optimization of queries
- Enable triggers and stored procedures
- Provision of key figures on the technology and process of the DBS