The Linux cat command is one of the most commonly used commands in Unix/Linux. The command is mostly used to view the contents of a file. Additionally, you can use the cat command to view multiple files at a go and even creating files and adding content to them. In this guide, we explore different ways that the command is used on Unix/Linux system. Buckle up!
Table of Contents
1. Basic syntax in cat command usage
The most basic usage of the syntax command is:
$ cat filename
For example, to view a file located in the current directory, for instance, linux_fundamentals.doc, run the command:
$ cat linux_fundamentals.doc
To view a file located on a different path, use the syntax
$ cat /path/to/file
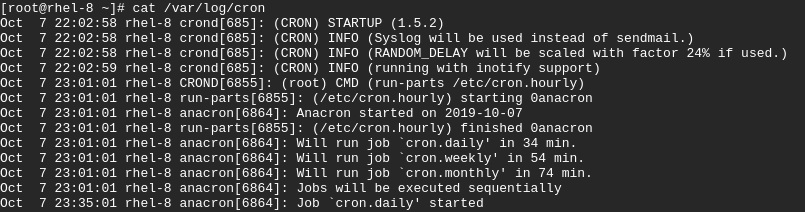
For instance, to view the file boot.log located in the path /var/log/cronrun
$ cat /var/log/cron
Sample output
2. Use cat command with ‘less’ or ‘more’ options
Sometimes, the output may be too long and oftentimes, you may be compelled to scroll up and down on the terminal, like in the previous example with /var/log/cron
To make your life easy, pipe the output to ‘less’ or ‘more’. This way, you can press ENTER and scroll at your own pace without worrying about missing some details.
$ cat /var/log/cron | less
3. View multiple files in a single command
To check the contents of multiple files in a single command use the syntax
$ cat file1 file2 file3
This saves you time and energy in running the command multiple times.
4. Print line numbers using -n option
To make your output easy to follow, you might consider numbering your output using the -n option as shown below:
$ cat -n filename
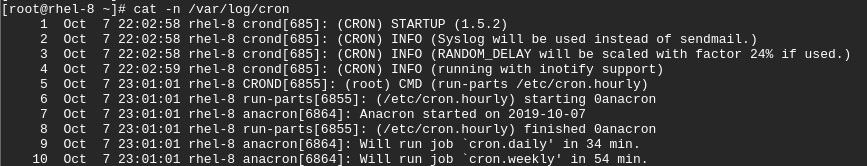
For example, to print line numbers in the /var/log/cronfile, run the command:
$ cat -n/var/log/cron
Sample output
5. Copy contents of one file to another
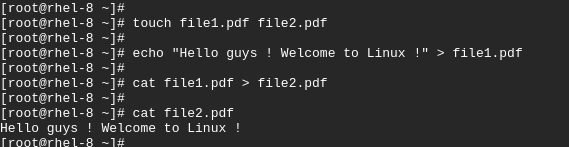
You can copy the contents of one file into another using the redirection operator greater than (>)
For example, to copy contents of file1.pdf to file2.pdf run
$ cat file1.pdf > file2.pdf
NOTE:
Care should be taken when using the greater than (>) redirection sign on an existing file because it overwrites already existing content in a file
To add or append content on another existing file, use the double greater than sign (>>) to avoid overwriting.
For example, to add content on file2.pdf run
$ cat file1.pdf >> file2.pdf
6. Create a new file using the cat command
Apart from viewing your files, overwriting and appending text, you can use the cat command to create a new line using the redirection operator greater than sign (>)
The syntax is shown below
$ cat > filename
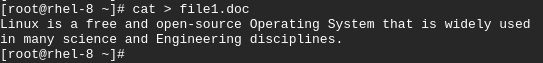
Once you run the command, Type the content and once done, press Ctrl + d to exit
$ cat > file1.doc
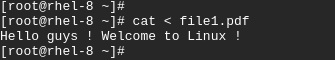
7. Read contents from a file
You can also read content from a file using the redirection operator less-than sign ( < )
$ cat < filename
For example,
$ cat < file1.doc
Conclusion
We have looked at the most commonly used cat command examples used both by Linux novices and advanced users. As you have seen these are simple to master and use at your convenience. The command is useful in viewing, reading, and creating files as well as performing other operations such as numbering output and redirection. We hope this guide was informative.

