Table of Contents
DMZ Definition
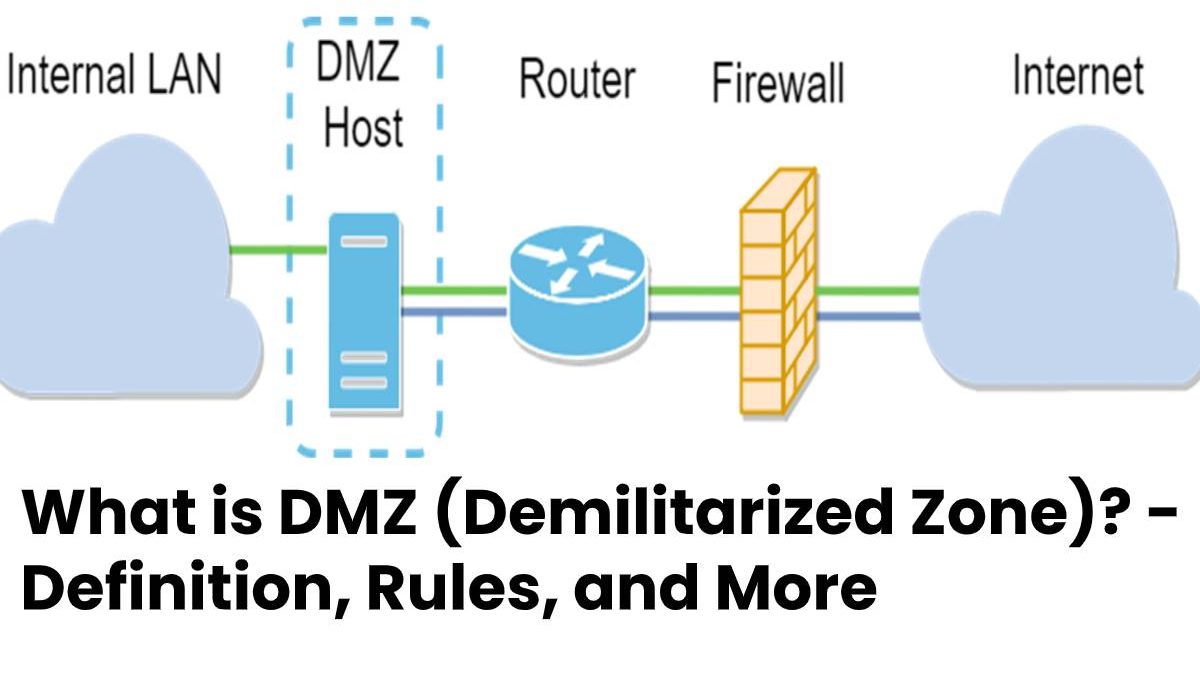
The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) is an independent network that acts as a buffer zone between an external network and the internal network.
The buffer network contains, for example, web servers or mail servers, the communication of which is monitored by firewalls.
It refers to a specially controlled network that locates between the external network (Internet) and the internal system.
It is a kind of buffer zone that separates the systems from one another by strict communication rules and firewalls.
Also Read: What is Stream Cipher? – Definition, Attacks, and More
What are the firewall rules in the demilitarized zone?
The rules on the firewall in conjunction with the demilitarized zone, provide the following communication options:
- Users from the Internet allow only to access servers in the demilitarized zone and not to resources of the internal network.
- As a rule, users from the internal system do not communicate directly with support from the Internet.
- For example, they access external resources via a proxy server, which, as a proxy, handles the Internet communication for them.
- The firewall rejects packets from the DMZ for which there are no corresponding input packets in the direction of the Internet and the internal network.
What is the DMZ with one or two firewalls?
- A demilitarized zone can implement with one or two firewalls. Ideally, these are firewalls from different manufacturers.
- If two firewalls used, there is one between the DMZ and the internal network (inner firewall) and between the DMZ and the external network (outer firewall).
- It prevents security gaps from allowing both firewalls to overcome at the same time.
- A more cost-effective solution is to implement the demilitarized zone with only one firewall.
- Demilitarized zone connects at least three network connections with the internal network, and also the external network.
What is a cheap alternative to the DMZ?
- Inexpensive routers, such as those used for private internet access, often advertise with DMZ support.
- If an exposed host constitutes, the router forwards traffic from the Internet that does not belong to existing connections to a single computer or server.
- And also, the exposed host does not separate from the LAN and offers no protective effect comparable to that in a DMZ.
Also Read: What is RPZ (Response Policy Zones)? – Definition, Advantages and More