As technology advances, the security of our data, systems, and devices are becoming an increasingly important issue for us. Cybersecurity is a hot topic nowadays that we need to talk about. This is where Common Criteria come into play. Never heard about it? Or are you not sure what it is and how it works? Do not worry, we’ve got you covered.
This article will discuss:
What are Common Criteria?
What are its key elements?
Benefits of Common Criteria Certification
What is EAL?
Ready to dive in? Then keep reading!
Table of Contents
What is Common Criteria?
Common Criteria are a framework of scalable and internationally accepted standards (ISO 15408) for cybersecurity certification. Common Criteria and its companion, the Common Methodology for Information Technology Security Evaluation (CEM) constitute the technical foundation for the Common Criteria Recognition Arrangement (CCRA), an international agreement that ensures:
- IT Products can only be evaluated by independent and competent accredited laboratories.
- Within the Common Criteria certification process, supporting documents are used to clarify how the criteria and evaluation techniques are utilized when evaluating and certifying individual technologies.
- A variety of Certificate Authorizing Schemes can offer certification of an assessed product’s security qualities, depending on the results of their evaluation.
- These certificates are accepted by all CCRA (Common Criteria Recognition Agreements) signatories (members of CCRA).
Key elements and their definitions
Here are some essential elements and their definitions to know when trying to comprehend Common Criteria:
- ISO/IEC 15408 – in its entirety this standard is meant to be used as the foundation for the evaluation of the safety properties of IT products.
- Target of Evaluation (TOE) – the IT system or product which is subject to the evaluation.
- Security Functional Requirements (SFRs) – define particular security functions that a product must offer. Common Criteria provide a list of such functions. An SFR, for example, may specify how a user with an exact role may be authenticated.
- Protection Profile (PP) – a document that outlines security criteria for a class of security devices (a certain group of products) and is usually set by a user or user community.
- Security Assurance Requirements (SARs) – these are descriptions of the steps done during the product’s development and assessment to ensure compliance with the stated security capabilities.
- Security Target (ST) – the documentation which specifies the security properties of the target of evaluation. The ST may assert conformance with one or more PPs. The TOE is measured against the SFRs defined in its ST. This enables suppliers to customize the evaluation to precisely match the capabilities of their product.
What are the benefits of Common Criteria Certification?
Common Criteria certification comes with multiple benefits. Here are some examples:
- Being accepted by all CCRA countries (31 at the moment) it releases the burden of duplicated IT product evaluations and security profiles;
- Guarantees that IT product and security profile evaluations are completed to consistently high standards;
- Boosts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the certification process for IT properties and protection profiles.
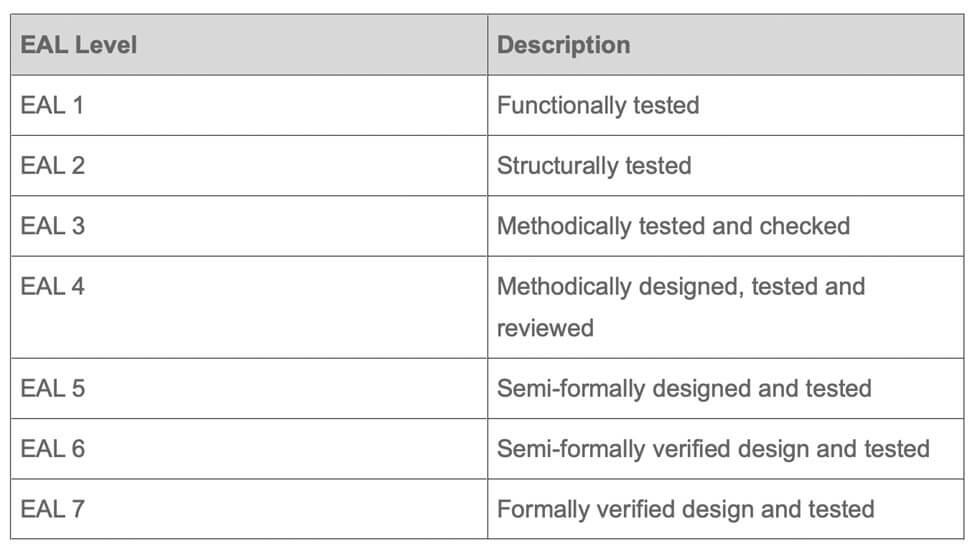
Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Levels
The Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL) is a category ranking given to an IT system or product after the Common Criteria security assessment. The level reflects the security level requirements to which the product or system was evaluated against. There are 7 EAL levels:
Conclusion
In summary, Common Criteria ensure that the definition, implementation, and assessment of an IT system or product was carried out in a strict, consistent, and repeatable way at an appropriate level for its environment. Common Criteria certification is received after successfully completing this process. We hope that our article gave you a better understanding of Common Criteria.

