IPv6 is nothing new. But it is now, with the growth of technologies like BYOD, IoT, mobile, cloud, etc that we are starting to see its value. Its predecessor, IPv4, is still essential for addressing across the Internet, but end-users are the first ones to begin the experience of IPv4 address exhaustion.
Table of Contents
What is an IPv6 proxy?
An IPv6 Proxy is any type of proxy that works using the IPv6 addressing protocol— rather than the IPv4 address, which is the common format nowadays. A proxy serves as an intermediary between two networks. It could be deployed between private and public (Internet) or vice versa. A proxy could also help separate two complex internal networks and make them more manageable and simple.
Scrape any website at scale in seconds with Geonode Proxy
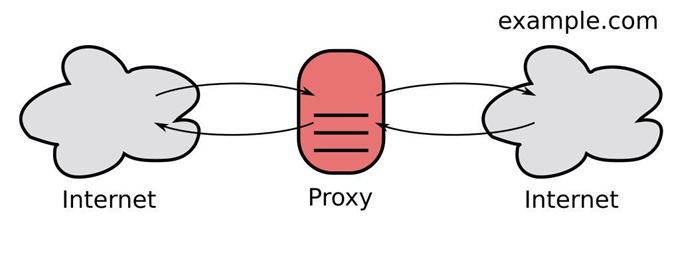
IPv6 proxies are getting popular mainly because IPv6 addresses are fresh, unused and cheaper than IPv4 addresses.
So, what is the problem with IPv4s? We are running out of IPv4 addresses. The new and fresh IPv4s are becoming a kind of rarity— they are very hard to get and if you do find IPv4 available, the prices are not always accessible. Generally, new IPv4s are assigned to ISPs and mobile carriers, and not really to end-users.
For the rest of IPv4s— a big percentage of them, are reused and recycled every single day. Although there is nothing wrong with reusing an IPv4 address that just gives you identity over the Internet, the problem is that you never know the history and reputation behind that IP. It may have been used by countless proxies to unlock Netflix or as part of a botnet. If it did have that kind of hard life… don’t be surprised when your Proxy with IPv4 meets up with constant bans.
What is not an IPv6 proxy?
Sometimes, the IPv6 proxy is also referred to as the IPv4 to IPv6 mapper (or IPv6 Gateway). This type of gateway does the mapping between an IPv4 and an IPv6 network, and usually works in dual-stack mode (IPv4 and IPv6). The IPv6 gateway receives an incoming request from an IPv4 network, going to an external resource and maps it to an IPv6 address.
The Advantages of IPv6 over IPv4.
The IPv6 protocol has definite advantages over the IPv4 protocol. Some of these advantages are the abundance of addresses, the direct addressing, its integrated interoperability, easier management, etc.
- Address abundance.
IPv6 provides an order of magnitude higher number of possible addresses (340 trillion trillion trillion IPv6 addresses). With IPv6, people could assign multiple IP addresses per interface for each of their devices.
- Direct addressing and end-to-end connectivity.
With IPv6, there is no need to deploy IP mapping strategies such as Network Address Translation (NAT).
- Integrated interoperability, security, and mobility.
IPv6 comes with built-in support for new demands like security (IPsec) and mobility.
- Easier management.
IPv6s are easier and more simple to manage for large deployments. IPv6 comes with auto-configuration capabilities.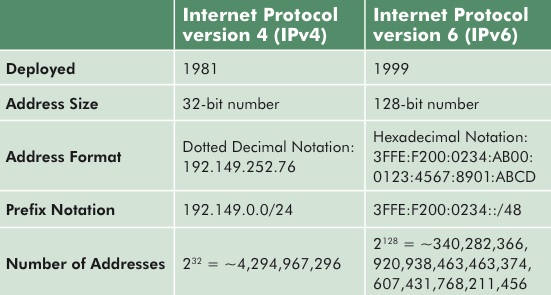
An advantage of IPv4 over IPv6? Although some Internet providers are already supporting IPv6, the entire Internet works on IPv4. In fact, there are many websites that still don’t offer support for IPV6. But, the historical trend in the percentage of websites using IPv6 shows a steady increase, and is very likely that it will continue increasing. Popular sites are already supporting IPv6, including: Google.com, Youtube.com, Facebook.com, yahoo.com, wikipedia.com, Netflix.com, Microsoft.com, and a lot more.
IPv6 Proxy: Six Applications.
Below are six possible applications for the IPv6 proxy server.
1. Web Scraping.
IPv6 proxies are fantastic options for your web scraping campaigns. You can extract data from search engines or any website without getting identified and banned. Use multiple IPv6 proxies or lists of proxies with your web scraping apps such as Scrapebox or through your own Python-based web scraper.
2. Improve and Scale SEO Campaigns.
Similar to web scraping, when doing intensive and large-scale SEO campaigns, any search engine or competition site may be capable of identifying and blocking your IP. Rotating IPv6 proxies ensure that your SEO efforts are not detected, and most important that they are effective, and fast.
3. Social Media Marketing.
Social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Youtube etc., are capable of identifying singular source IPs with multiple accounts. These platforms will suspend accounts that are linked to an IP generating unusual traffic. IPv6 proxies help SMM companies, open and manage multiple accounts, commenting, testing ads, unblock geo-restricted content, and more.
4. Unblocking Geo-restricted Content.
Companies dealing with copyrights content or targeting specific audiences, such as Netflix, Hulu, and HBO will usually tailor the content to that specific audience based on geography. Proxies deployed in different countries will help give access to that particular content. It will help bypass those geo-restrictions.
5. Maximize Online Privacy.
IPv6 HTTPS and SOCKS5 proxies will maximize your online privacy. They are great alternatives to hide your IP without compromising performance and speed. Whether you want an anonymous web browsing experience via an HTTPs IPv6 proxy or to use a resource-demanding application like torrenting or streaming, via a SOCKS5 IPv6 proxy.
6. Bypass Censorship and Network Constraints.
A firewall may be blocking specific portions of your traffic going towards certain destinations, for example Wikipedia, BBC, Facebook, Youtube, etc. But a firewall doesn’t know about the IPv6 proxy, which is forwarding requests (and probably encrypting data) to the target destination. IPv6 proxies are the best solution for bypassing censorship and network constraints.
Final Words.
The IPv6 proxy differs from the IPv4 proxy, only in its addressing protocol. But this is a huge difference especially, when it comes to online anonymity and privacy. It is much easier and cheaper to get your hands on entire blocks of new IPv6 addresses that have never been used, rather than getting your hands on fresh IPv4s.
IPv6 proxies can be very efficient for applications like: web scraping, improve and scale SEO campaigns, social media marketing, unblocking geo-restricted content, maximize online privacy, and bypassing censorship and network constraints.

